Implementing accounts in Tally
Implementing Accounts in Tally - Basics of Accounting, Golden Rules of Accounting, Voucher Entry, Ledger Posting, Final Accounts Preparation
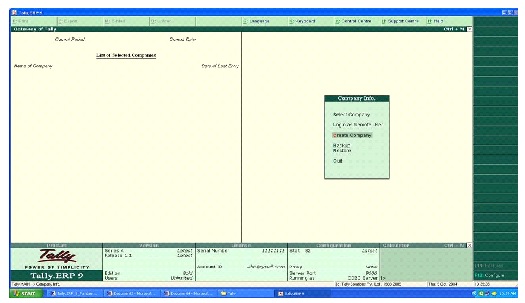
Tally Software : In Gateway of Tally the following option is display.
Screen of the Tally
Tally Screen: Tally screen can be divided into following four broad parts.
1. Product info
2. Button bar
3. Calculator
4. Work area
Product info: Product info bar in Tally.ERP9 consisting of the information about the product.
1. Developer company
2. Software version and Release
3. Software Serial Number
4. Single or Multiple User
5. System Day and Date
6. System Time
Button Bar: Buttons appearing in the button bar (at right of the screen) provide quick access to different options. Buttons on the button bar is context sensitive, different buttons appear at different screens.
Calculator: By default the work area becomes active and calculator remains inactive. Press Ctrl + N that would activate the calculator when calculator is active, we can enter value and operators.
The calculator follows BODMAS rule that indicates the execution sequence: Bracket, Power, Division,
Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction.
Work area
The work at Gateway is broadly separated into two sections.
- The right hand side contains the popup menu, where we would select instructions to Tally.
- The left hand side displays list of selected companies.
On left part of the screen
Current Period
Financial period with which we are working is displayed for reference. To change the Financial period click
"F2:period" button in the button bar or press <Alt> + <F2>.
Current Date
It is not the calendar date but the date we worked last during the current period. Vouchers will have the same date as of current date. To change current date click "F2:Date" button in the button bar or press F2.
List of selected companies
Name of all selected companies with last date voucher entry is displayed here. If we select more than one company, the active company is shown at the top of list in bold face and others appear next in normal fonts.
On right part of the screen
Gateway of Tally menu
Primary choices of menu is displayed. The menu operations are dependent on selection/activation of operations. In some cases, we may find some operations grayed indication that the option is not active.
For example, upon selecting a company maintaining Accounts only, Inventory Info and stock summary options would be grayed.
Selections of menu
We can select a menu in either of the following mode:
- Press the highlighted character. For example, to select create company, press 'C' the highlighted character.
- Move highlight bar on the option with Up/Dn arrow key and press<Enter>.
- Using mouse double click the option. (We have to click twice very fast).
Company Info Menu
On loading Tally, by default, Company Info menu appear to select a company we wish to work with. If we are installing Tally first time. select company option would remain inactive and by default cursor would appear on Create Company option.
Buttons at gateway
Help (Hotkey: Alt+H): This button launches "Tally Reference Manual. This is a compiled HTML Help file. Normally on clicking this button, the relevant content in respect of the screen would be displayed. If no context sensitive Help exists, contents would be displayed. We can select the topic we wish to view.
Web browser (Hot key: Alt+W)
This button launches the default installed web browser. For example, internet explorer is the default web browser, on clicking the button IE will be loaded. The browser will appear within the work area of the tally screen. All other areas of Tally screen still remains in the screen.
F1- Select cmp (Hoy key: F1)
This button will display the list of companies. Move the highlight bar and press <Enter> key to select a particular company. Or simply press F1 key on the keyboard.
Introduction to Accounting
It is the language of business through which normally a business house communicates with the outside world
Accounting and accountancy are often synonymous terms.
Accounting can be classified into two parts.
- Financial accounting
- Management Accounting
Financial Accounting
The accounting for revenues, expenses assets and liabilities that is commonly carried on in the general offices of a business is termed as Financial Accounting.
Its aim is to ascertain the profit or loss and to state the financial position of the business as at a particular date.
Scope of Financial Accounting
- Recording information in account books like journals, cashbooks etc
- Classifying the accounts using ledger.
- Summarising the information as statements like (1) Trial balance (2) Income statement and (3) Balance sheet
Management Accounting
The term management accounting refers to accounting for the management. The management accounting provides information to the management so that planning, organising directing and controlling of business operations can be done in an orderly manner.
Scope of Management Accounting
Following areas are identified within management accounting
- Financial accounting
- Cost accounting
- Revaluation accounting
- Budgetary control
- Inventory control
- Statistical methods
- Interim Reporting
- Taxation
- Office services
- Internal Audit
Accounting terms
Business transaction
A business transaction is "The movement of money and money's worth form one person to another" or exchange of values between two parties.
Purchase means goods purchased by a businessman from suppliers.
Sales is goods sold by a businessman to his customers.
Purchase Return or Rejection in or Outward Invoice
Purchase return means the return of the full or a part of goods purchased by the businessman to his suppliers. Sales Return or Rejection out or Inward Invoice
Sales return means the return of the full or a part of the goods sold by the customer to the businessman.
Assets
Assets are the things and properties possessed by a businessman in business.
Two types of Assets
Fixed Asset means the asset remain in business of use and not for resale. Eg. A shop owner purchase buildings, typewriter, showcases
Current Asset means the things and properties for resale ie. The asset converts into cash. Eg. A cloth shop owner buys cloth for resale. Stock of cloth is current asset.
Liabilities
All the amounts payable by a business concern to outsiders are called liabilities.
Capital
Capital is the amount invested for starting a business by a person.
Debtor
Debtor is the person who receives benefit without giving money or moneys worth immediately, but liable to pay in future. i.e. the person owes amounts to the businessman. Creditor
Creditor is the person who gives benefit without receiving money or money's worth immediately but ot claim in future. i.e. the personto whom amounts are owed by the businessman.
Debit: The receiving aspect of a transaction is called debit or Dr.
Credit: The giving aspect of a transaction is called credit or Cr.
Drawings
Drawings are the amounts withdrawn (taken back) by the businessman from his business for his personal, private and domestic purpose. Drawings may be made in the form cash, goods and assets of the business.
Receipts
It is a document issued by the receiver of cash to the giver of cash acknowledging the cash received voucher.
Account
Account is a summarized record of all the transactions relating to every person, everything or property and every type of service.
Ledger
Ledger is the main book of account. It is the book of final entry where accounts lie.
Journal
Journal is a book of first entry. Transactions are entered in the journal before taken to the appropriate ledger accounts.
Trial Balance
It is a statement of all the ledger account balances prepared at the end of particular period to verify the accuracy of the entries made in books of accounts.
Profit
Excess of credit side total amount over debit side total amount.
Loss
Excess of debit side total amount over credit side total amount.
Profit and loss account
It is prepared to ascertain actual profit or loss of the business.
Balance Sheet
To ascertain the financial position of the business. It is a statement of assets and liabilities.
Types of accounts
Accounts can be divided into two major types.
Personal Accounts
Impersonal Accounts
Impersonal Accounts can be further divided into two types.
- Real Account
- Nominal Account
Personal accounts are the accounts of persons, firms, concerns and institutions which the businessmen deal. Principles: Debit the receiver, Credit the giver
Real Account: These are the accounts of things, materials, assets & properties. It has physical existence which can be seen & touch. Ex. Cash, Sale, Purchase, Furniture, Investment etc.
Principles: Debit what comes in, Credit what goes out
Nominal account: Nominal account is the account of services received (expenses and Losses) and services given (income and gain) Ex. Salary, Rent, Wages, Stationery etc.
Principles: Debit all expense/losses, Credit all income/ gains
- Log in to post comments